Moles are common skin growths that vary in color, size, and shape. While many people have moles, some may consider removal for cosmetic reasons or due to concerns about potential skin cancer. Understanding the options for mole removal, the factors influencing whether a mole can be removed, and the associated risks is crucial for anyone considering this procedure. This article will provide an in-depth exploration of mole removal, helping you make informed decisions regarding your skin health.
Understanding Moles
Moles, or nevi, are typically benign growths formed by clusters of melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin pigmentation. Moles can appear anywhere on the body and may change in appearance over time. While most moles are harmless, certain characteristics may warrant further evaluation by a dermatologist.
Types of Moles
-
Common Moles: Typically round or oval, these moles are usually brown or black and generally harmless.
-
Atypical Moles: Larger than average and often irregular in shape or color, these moles may have an increased risk of developing into melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer.
-
Congenital Moles: Present at birth, these moles can vary in size and may require monitoring or removal depending on their characteristics.
-
Dysplastic Nevi: These moles have irregular features and may indicate a higher risk of melanoma. Regular monitoring is essential.
Reasons for Mole Removal
While not all moles require removal, several factors may lead an individual to consider this option:
- Cosmetic Concerns: Many people seek to remove moles that are raised, discolored, or positioned in a way that causes self-consciousness.
- Potential Health Risks: A mole that changes in appearance, size, or color may indicate underlying issues. Dermatologists often recommend removal for biopsy if there's a concern about skin cancer.
- Irritation: Moles located in areas prone to friction, such as underarms or the waistline, may become irritated and lead to discomfort.
Can All Moles Be Removed?
Medical Considerations
Not all moles are suitable for removal, and several medical considerations influence the decision:
-
Type of Mole: Common moles can typically be removed easily, while atypical moles may require careful evaluation to determine the best approach.
-
Location: Moles in sensitive areas, such as the face or genital region, may require specialized techniques to minimize scarring and ensure a successful outcome.
-
Size and Depth: Larger moles may be more challenging to remove completely, and the depth of the mole can impact the technique used.
-
Patient Health: Certain medical conditions or skin types may influence the feasibility of mole removal. Individuals with specific skin conditions or a history of keloid scarring may require a tailored approach.
Types of Removal Techniques
When considering mole removal, various techniques are available, each with its own advantages and limitations:
-
Excision: In this method, the mole is cut out along with a margin of surrounding skin. This technique is often used for moles that are suspected to be cancerous, as it allows for thorough examination of the tissue. Excision may leave a scar, but it typically provides a clear margin to prevent recurrence.
-
Shave Removal: This technique involves shaving off the mole at skin level using a scalpel. Shave removal is less invasive and often preferred for cosmetic moles. However, it may not be suitable for deeper or atypical moles.
-
Laser Removal: Lasers can be used to break down the pigment in certain types of moles. This technique is primarily cosmetic and may not be effective for all moles, especially those that require deeper removal or biopsy.
-
Cryotherapy: Freezing the mole with liquid nitrogen can cause it to fall off. This method is primarily used for superficial growths and may not be suitable for all mole types.
-
Electrosurgery: This method uses an electric current to cut away the mole and coagulate the surrounding tissue. It is often used for smaller, benign moles.
Factors Influencing Mole Removal Decisions
1. Dermatologist Evaluation
Before proceeding with mole removal, a thorough evaluation by a dermatologist is essential. During the consultation, the doctor will assess the mole’s characteristics, discuss your medical history, and consider factors such as:
- Changes in size, color, or shape
- Family history of skin cancer
- Skin type and healing capacity
2. Risk of Skin Cancer
If a mole shows signs of atypical features, the dermatologist may recommend biopsy before removal. This involves taking a small sample of the mole to examine it for cancerous cells. Based on the results, the doctor will advise on the appropriate course of action.
3. Personal Preferences
Individual preferences play a significant role in the decision to remove a mole. Some people may prioritize cosmetic improvements, while others may focus on medical concerns. A thorough discussion with your dermatologist will help align your goals with appropriate options.
Risks and Considerations
While mole removal is generally safe, it is essential to understand the associated risks, which may include:
- Scarring: All removal techniques carry a risk of scarring. Excision, in particular, may result in more noticeable scars, depending on the size and location of the mole.
- Infection: Any surgical procedure poses a risk of infection. Following proper aftercare instructions can help minimize this risk.
- Recurrence: In some cases, moles may grow back after removal, particularly if not fully excised. Regular follow-up appointments are vital for monitoring any changes.
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to topical medications or anesthetics used during the procedure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can I remove my moles at home?
Home removal methods are not recommended due to safety and effectiveness concerns. Always consult a dermatologist for professional evaluation and treatment.
2. How much does mole removal cost?
Costs vary based on the removal method, location, and whether the procedure is deemed cosmetic or medical. Consult your dermatologist for an accurate estimate.
3. Will I need stitches after mole removal?
Stitches may be required if the mole is excised. Your dermatologist will inform you about the specifics during your consultation.
4. How long does it take to recover from mole removal?
Recovery time depends on the removal method but generally ranges from a few days to a couple of weeks.
5. Can I go back to normal activities after mole removal?
Most individuals can resume normal activities shortly after the procedure, but it's advisable to avoid strenuous exercise for a week.
6. What should I do if the mole grows back?
If a mole grows back after removal, contact your dermatologist for further evaluation and treatment.
7. Are there any permanent side effects of mole removal?
Potential side effects include scarring or changes in skin pigmentation. Discuss these risks with your dermatologist.
8. Is mole removal covered by insurance?
Insurance coverage depends on whether the removal is deemed medically necessary or cosmetic. Check with your insurance provider for specifics.
9. What is the best method for mole removal?
The best method varies by individual and mole type. A dermatologist can recommend the most appropriate option based on your specific situation.
10. How can I prevent new moles from forming?
While some moles are genetic and cannot be prevented, protecting your skin from sun exposure and maintaining overall skin health can reduce the risk.
In summary, while many moles can be safely removed, the decision to do so should be based on a thorough evaluation by a qualified dermatologist. Understanding the different removal techniques, the factors influencing the decision, and the associated risks will empower you to make informed choices about your skin health. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of action for your specific needs.
 Clinic Booking
Clinic Booking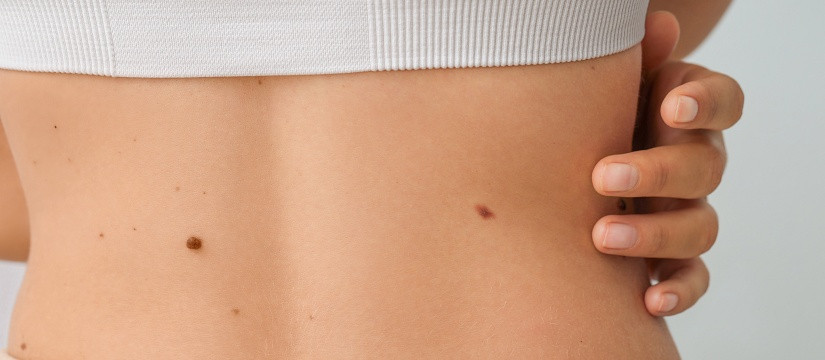


 No Record
No Record