A tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the tonsils, two lymphoid tissues located at the back of the throat. This procedure is commonly performed to alleviate various health issues associated with the tonsils. Understanding the reasons for tonsillectomy is essential for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers. This article provides an in-depth overview of the common reasons for needing a tonsillectomy, including medical conditions, symptoms, and considerations that lead to this surgical intervention.
1. Recurrent Tonsillitis
1.1 Definition
Tonsillitis is the inflammation of the tonsils, typically caused by viral or bacterial infections. Symptoms often include:
- Sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Swollen tonsils
- Fever
- Bad breath
- Ear pain
1.2 Indications for Surgery
Recurrent tonsillitis can significantly impact a person's quality of life. The criteria for tonsillectomy often include:
Frequency of Infections: Patients who experience:
- More than seven episodes of tonsillitis in one year.
- Five episodes per year over two consecutive years.
- Three episodes per year over three consecutive years.
Impact on Daily Life: If tonsillitis leads to missed school or work days, increased healthcare visits, or prolonged illness, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Complications: Recurrent tonsillitis can result in complications such as:
- Peritonsillar abscess: A collection of pus that forms near the tonsils, causing severe pain and swelling.
- Chronic pain: Persistent sore throat that affects eating and daily activities.
2. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
2.1 Definition
Obstructive sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep due to obstruction of the upper airway. Enlarged tonsils can be a significant contributing factor.
2.2 Symptoms of OSA
Patients with obstructive sleep apnea may exhibit symptoms such as:
- Loud snoring
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Morning headaches
- Difficulty concentrating
2.3 Indications for Surgery
- Enlarged Tonsils: If enlarged tonsils are causing airway obstruction, tonsillectomy may be recommended. Removing the tonsils can help alleviate symptoms of OSA and improve overall sleep quality.
- Impact on Health: OSA can lead to serious health issues, including cardiovascular problems, high blood pressure, and metabolic disorders. Tonsillectomy can mitigate these risks by improving airflow during sleep.
3. Difficulty Swallowing
3.1 Definition
Enlarged tonsils can lead to significant discomfort and difficulty swallowing, impacting a person’s ability to eat and drink comfortably.
3.2 Symptoms of Difficulty Swallowing
Patients may experience:
- Pain while swallowing
- A sensation of obstruction in the throat
- Drooling or inability to swallow certain foods
3.3 When is Surgery Recommended?
- Persistent Symptoms: If difficulty swallowing due to enlarged tonsils significantly affects nutrition and quality of life, tonsillectomy may be warranted.
- Weight Loss or Malnutrition: In severe cases, patients may experience weight loss or nutritional deficiencies as a result of the inability to swallow properly.
4. Peritonsillar Abscess
4.1 Definition
A peritonsillar abscess is a painful condition characterized by a collection of pus near the tonsils, often resulting from untreated tonsillitis.
4.2 Symptoms of Peritonsillar Abscess
Common symptoms include:
- Severe sore throat, often worse on one side
- Difficulty opening the mouth (trismus)
- Swelling in the throat or neck
- Fever
- Bad breath
4.3 Indications for Surgery
- Recurrent Abscesses: If a patient has a history of multiple peritonsillar abscesses or experiences one that does not respond to treatment, tonsillectomy may be necessary to prevent future abscesses.
- Failure of Medical Treatment: If antibiotics and other treatments fail to resolve the abscess, surgical removal of the tonsils can be a definitive solution.
5. Chronic Tonsil Stones
5.1 Definition
Tonsil stones, or tonsilloliths, are calcifications that form in the crevices of the tonsils. They can cause a range of symptoms, including bad breath and discomfort.
5.2 Symptoms of Tonsil Stones
Patients may experience:
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Ear pain
5.3 When is Surgery Recommended?
- Frequent Formation: If tonsil stones occur frequently and cause ongoing discomfort or bad breath, tonsillectomy may be a suitable option to eliminate the source of the problem.
- Impact on Quality of Life: For individuals who find tonsil stones disruptive to their daily life or self-esteem, surgery can provide relief.
6. Other Considerations for Tonsillectomy
6.1 Tumors or Malignancy
- Suspicion of Cancer: In rare cases, if there are signs of tumors or malignancy in the tonsils, surgical removal may be necessary for diagnosis and treatment.
6.2 Immune System Concerns
- Chronic Infections: For patients with compromised immune systems who suffer from frequent tonsil infections, a tonsillectomy may help reduce the frequency of infections and improve overall health.
Tonsillectomy is a common surgical procedure performed to address various health issues associated with the tonsils, including recurrent tonsillitis, obstructive sleep apnea, difficulty swallowing, chronic tonsil stones, and peritonsillar abscesses. Understanding the common reasons for needing a tonsillectomy can help patients and their caregivers make informed decisions about their health. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms that may indicate the need for a tonsillectomy, consulting a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and discussion of treatment options is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a tonsillectomy?
A tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the tonsils, typically performed to treat recurrent tonsillitis, obstructive sleep apnea, and other complications.
2. What are the signs that I might need a tonsillectomy?
Signs include frequent sore throats, difficulty swallowing, excessive snoring or gasping during sleep, and the presence of tonsil stones.
3. How many times do I need to have tonsillitis for surgery to be considered?
Surgery may be considered if you experience more than seven episodes of tonsillitis in one year, five episodes per year over two years, or three episodes per year over three years.
4. Can tonsillectomy help with sleep apnea?
Yes, tonsillectomy can help alleviate obstructive sleep apnea symptoms in individuals whose enlarged tonsils block the airway during sleep.
5. What are the risks of tonsillectomy?
Risks include bleeding, infection, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. Discuss these risks with your healthcare provider before surgery.
6. What is the recovery time after a tonsillectomy?
Initial recovery typically takes about 1 to 2 weeks, but complete healing may take several weeks. Follow your healthcare provider's advice for post-operative care.
7. Can I eat normally after a tonsillectomy?
During the initial recovery phase, it's best to stick to soft foods and avoid spicy, crunchy, or acidic foods until the throat has healed.
8. What should I do if I notice complications after surgery?
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience excessive bleeding, severe pain, or signs of infection such as fever.
9. Is tonsillectomy a common procedure?
Yes, tonsillectomy is one of the most common surgical procedures performed in children and is also performed in adults when necessary.
10. How can I prepare for a tonsillectomy consultation?
Before your appointment, make a list of your symptoms, any medications you are taking, and any previous treatments you've undergone for tonsil issues. This information will help your healthcare provider make an informed recommendation.
 Clinic Booking
Clinic Booking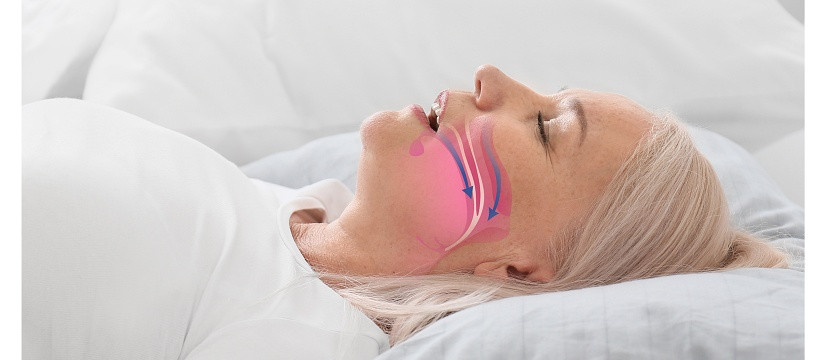


 No Record
No Record