Varicose veins are a common condition that can cause discomfort, pain, and cosmetic concerns. While surgical options exist to address these veins, many patients prefer non-surgical treatments that are minimally invasive and require less recovery time. This article explores the various non-surgical treatment options available for varicose veins, their effectiveness, and considerations for choosing the right approach.
1. Understanding Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments for varicose veins aim to alleviate symptoms, improve appearance, and promote better vein function without the need for invasive surgery. These methods typically involve minimally invasive techniques that can be performed in an outpatient setting.
2. Common Non-Surgical Treatments
A. Sclerotherapy
What It Is
Sclerotherapy involves injecting a sclerosant solution directly into the affected veins. This solution causes the vein to collapse and eventually fade from view.
Effectiveness
- Success Rate: Sclerotherapy has a high success rate, with many patients seeing significant improvements after one or more treatments.
- Time Frame: The treated veins typically become less visible over several weeks to months as the body gradually absorbs them.
Considerations
- Number of Sessions: Some patients may require multiple sessions for optimal results, especially for larger or more extensive veins.
- Side Effects: Possible side effects include bruising, redness, and swelling at the injection site.
B. Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT)
What It Is
EVLT is a minimally invasive procedure that uses laser energy to close off varicose veins. A small catheter is inserted into the vein, and laser energy is delivered to seal it shut.
Effectiveness
- Recovery: Patients can often resume normal activities within a day or two after the procedure.
- Results: Many patients experience a significant reduction in symptoms and improvement in the appearance of the treated veins.
Considerations
- Multiple Treatments: Some patients may require more than one treatment, particularly for larger veins.
- Side Effects: Common side effects can include temporary pain, bruising, and swelling in the treated area.
C. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
What It Is
Radiofrequency ablation uses radiofrequency energy to heat and close off varicose veins. Similar to EVLT, a catheter is inserted into the vein, delivering controlled heat to seal it shut.
Effectiveness
- Results: RFA has a high success rate, and patients often notice significant improvements shortly after treatment.
- Minimal Downtime: Like EVLT, RFA allows patients to return to their daily activities relatively quickly.
Considerations
- Side Effects: Patients may experience discomfort, swelling, or bruising after the procedure, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days.
D. Foam Sclerotherapy
What It Is
Foam sclerotherapy is a variation of traditional sclerotherapy that uses a foamed sclerosant solution, which is more effective for larger veins. The foam can better fill the vein and come into contact with the vessel wall.
Effectiveness
- Visual Improvement: Patients often see quicker and more noticeable improvements in vein appearance compared to standard liquid sclerotherapy.
- Multiple Sessions: As with traditional sclerotherapy, multiple sessions may be needed for optimal results.
Considerations
- Side Effects: Potential side effects include discomfort, bruising, and temporary changes in skin color at the injection site.
E. Compression Therapy
What It Is
Compression therapy involves wearing specially designed stockings that apply pressure to the legs, improving blood circulation and reducing the symptoms associated with varicose veins.
Effectiveness
- Symptom Relief: Compression stockings can alleviate discomfort, swelling, and fatigue in the legs, particularly during prolonged periods of sitting or standing.
- Prevention: This method is often recommended for patients at risk of developing varicose veins or for those recovering from surgery.
Considerations
- Consistency: For best results, patients should wear compression stockings regularly, especially during the day and when engaging in activities.
F. Lifestyle Modifications
What It Is
Incorporating lifestyle changes can significantly impact the management and prevention of varicose veins.
Effectiveness
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce pressure on the veins.
- Regular Exercise: Activities that promote leg movement, such as walking, can improve circulation and help prevent new varicose veins.
Considerations
- Long-Term Commitment: These lifestyle modifications should be viewed as ongoing efforts to promote overall vein health.
3. Choosing the Right Treatment
A. Consult with a Healthcare Provider
- Personalized Evaluation: It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or a vascular specialist to assess your condition and determine the most appropriate treatment option.
- Discuss Goals: Clearly communicate your symptoms, treatment goals, and concerns to receive tailored recommendations.
B. Consideration of Factors
- Severity of Condition: The extent and severity of your varicose veins can influence the choice of treatment.
- Lifestyle and Preferences: Consider your lifestyle, preferences for treatment, and the associated downtime when making a decision.
Non-surgical treatments for varicose veins provide effective options for individuals seeking relief from symptoms and improved vein appearance without the need for invasive surgery. Options such as sclerotherapy, EVLT, RFA, and compression therapy can significantly alleviate discomfort and enhance quality of life. By consulting with a healthcare provider and considering individual circumstances, patients can make informed choices about the best treatment approach for their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Are non-surgical treatments for varicose veins effective?
Yes, non-surgical treatments like sclerotherapy, EVLT, and RFA have high success rates in relieving symptoms and improving vein appearance.
2. How long does it take to see results from non-surgical treatments?
Results can vary, but many patients notice improvements within a few weeks to months after treatment, depending on the specific method used.
3. Are non-surgical treatments painful?
Most non-surgical procedures are minimally painful, with many patients reporting only mild discomfort during and after treatment.
4. How many treatment sessions will I need?
The number of sessions required can vary based on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment. Some patients may achieve results in one session, while others may need multiple treatments.
5. Can I return to normal activities after non-surgical treatment?
Most patients can return to their normal activities shortly after treatment, especially with minimally invasive procedures. However, you should follow your healthcare provider's specific recommendations.
6. Will insurance cover non-surgical treatments for varicose veins?
Coverage can vary depending on your insurance policy and whether the treatment is deemed medically necessary. It’s advisable to check with your insurance provider before proceeding.
7. How can I prevent new varicose veins after treatment?
Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and wearing compression stockings can help prevent the formation of new varicose veins.
8. Are there any side effects associated with non-surgical treatments?
Common side effects can include bruising, swelling, and temporary discomfort at the treatment site, but these typically resolve quickly.
9. Can lifestyle changes alone manage varicose veins?
While lifestyle changes can significantly improve vein health and reduce symptoms, they may not eliminate existing varicose veins. Non-surgical treatments may be necessary for significant improvement.
10. Is sclerotherapy safe for pregnant women?
Sclerotherapy is generally not recommended during pregnancy. It’s essential to consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
 Clinic Booking
Clinic Booking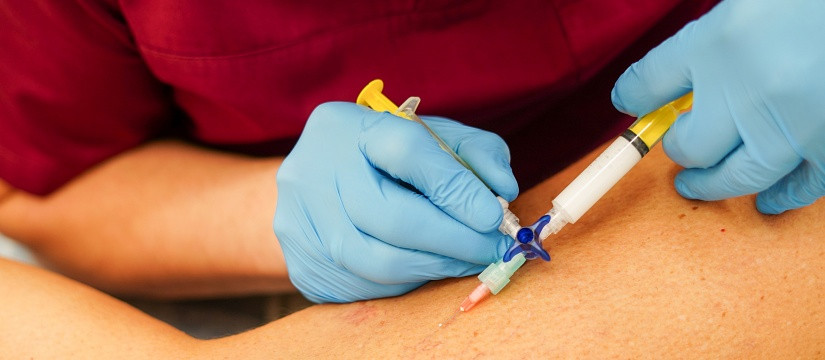


 No Record
No Record