Sleep disorders can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, physical health, and mental well-being. Fortunately, various treatment options are available to address these issues, ranging from lifestyle changes and behavioral therapies to medications and medical devices. This comprehensive guide explores the different treatment options for common sleep disorders, helping you understand how to find relief.
1. Lifestyle Changes
Making adjustments to your daily routine and environment can have a profound impact on sleep quality.
Sleep Hygiene:
Practicing good sleep hygiene involves establishing healthy sleep habits, such as:
- Keeping a consistent sleep schedule (going to bed and waking up at the same time daily).
- Creating a relaxing bedtime routine (reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques).
- Limiting screen time and exposure to blue light before bed.
- Ensuring your sleep environment is dark, quiet, and cool.
Dietary Modifications:
Your diet can influence sleep quality. Consider the following:
- Avoid Stimulants: Limit caffeine and nicotine intake, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime.
- Limit Alcohol: While alcohol may initially make you feel sleepy, it can disrupt sleep later in the night.
- Eat Light: Avoid heavy meals close to bedtime; opt for a light snack if needed.
Exercise:
Regular physical activity can promote better sleep, but timing matters. Aim for:
- Daily Exercise: Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Timing: Avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it may hinder your ability to fall asleep.
2. Behavioral Therapies
Behavioral therapies can help address the underlying behaviors and thoughts that contribute to sleep disorders.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I):
CBT-I is a structured program that helps individuals identify and change thoughts and behaviors that affect sleep. Key components include:
- Sleep Restriction: Limiting time spent in bed to increase sleep efficiency.
- Stimulus Control: Associating the bed with sleep (only using the bed for sleep and intimacy).
- Cognitive Restructuring: Challenging negative thoughts about sleep.
Relaxation Techniques:
Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation can help reduce anxiety and promote relaxation before bedtime.
Sleep Hygiene Education:
Learning about proper sleep hygiene practices can empower individuals to make positive changes that enhance sleep quality.
3. Medications
In some cases, medications may be necessary to treat sleep disorders. The type of medication prescribed will depend on the specific sleep disorder.
Insomnia Medications:
Short-term use of sedative-hypnotics may be prescribed for insomnia. Common options include:
- Benzodiazepines: Such as lorazepam (Ativan) and temazepam (Restoril), which promote sleep but may lead to dependency with long-term use.
- Non-benzodiazepine Sleep Medications: Such as zolpidem (Ambien) and eszopiclone (Lunesta), which are less likely to cause dependency.
Sleep Apnea Treatments:
For obstructive sleep apnea, treatment options may include:
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): A device that delivers a steady stream of air to keep the airway open during sleep.
- Oral Appliances: Dental devices designed to reposition the jaw and tongue to keep the airway open.
Narcolepsy Medications:
Medications for narcolepsy may include:
- Stimulants: Such as modafinil (Provigil) or amphetamines to promote wakefulness during the day.
- Sodium Oxybate: Used to treat excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy.
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) Treatments:
Medications for RLS may include:
- Dopamine Agonists: Such as pramipexole (Mirapex) and ropinirole (Requip), which can help alleviate symptoms.
- Iron Supplements: If iron deficiency is contributing to RLS, supplementation may be recommended.
4. Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief from sleep disorders through alternative therapies. While more research is needed, these approaches can complement traditional treatments.
- Acupuncture:
Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help improve sleep quality and reduce insomnia symptoms. - Herbal Remedies:
Natural remedies such as valerian root, chamomile, and melatonin supplements may promote sleep. Always consult a healthcare provider before trying herbal supplements, as they can interact with medications. - Mind-Body Techniques:
Practices like yoga, tai chi, and mindfulness meditation can reduce stress and promote relaxation, potentially improving sleep.
5. Sleep Environment Modifications
Improving your sleep environment can greatly enhance your ability to fall and stay asleep.
- Comfortable Mattress and Bedding:
Ensure your mattress and pillows provide adequate support and comfort. The right bedding can also help regulate temperature. - Minimize Disruptions:
Consider using blackout curtains to eliminate light, earplugs to reduce noise, and a white noise machine to create a calming sound environment. - Temperature Control:
Keep your bedroom cool (around 60-67°F or 15-19°C) to facilitate better sleep.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Follow-Up
For individuals with chronic sleep disorders, ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are essential for managing symptoms effectively.
- Regular Check-Ups:
Schedule regular appointments with your healthcare provider to discuss your progress, treatment efficacy, and any new symptoms that may arise. - Adjustments to Treatment Plans:
Be open to adjustments in your treatment plan based on your response to therapies and any changes in your sleep patterns. - Utilize Support Networks:
Joining support groups for sleep disorders can provide additional resources, encouragement, and shared experiences.
Treating sleep disorders involves a multi-faceted approach that includes lifestyle changes, behavioral therapies, medications, alternative therapies, and environmental modifications. If you suspect you have a sleep disorder, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Prioritizing sleep health is crucial for overall well-being, so taking proactive steps to address sleep issues can lead to significant improvements in quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are common treatments for insomnia?
Common treatments for insomnia include cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), sedative medications, and lifestyle changes to improve sleep hygiene.
How is sleep apnea treated?
Sleep apnea is often treated with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, oral appliances, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgery.
Are there medications specifically for narcolepsy?
Yes, medications such as stimulants (modafinil) and sodium oxybate are commonly prescribed to manage narcolepsy symptoms.
Can lifestyle changes really improve sleep disorders?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, and engaging in regular physical activity can significantly improve sleep quality.
What role do alternative therapies play in treating sleep disorders?
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and herbal remedies, can complement traditional treatments, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new therapy.
Is it necessary to undergo a sleep study?
A sleep study may be necessary for diagnosing certain sleep disorders, especially if symptoms suggest conditions like sleep apnea or narcolepsy. Your healthcare provider will determine if this is needed.
How long does it take to see improvements after starting treatment for a sleep disorder?
The timeline for improvement varies based on the type of disorder and treatment approach. Some individuals may notice improvements within a few days, while others may take several weeks.
Can children have sleep disorders?
Yes, sleep disorders can affect individuals of all ages, including children. Common issues in children include insomnia, sleep apnea, and night terrors.
Are there risks associated with using sleep medications?
Yes, sleep medications can have side effects and risks, including dependency, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms. Always discuss potential risks with your healthcare provider.
How can I support someone with a sleep disorder?
Supporting someone with a sleep disorder involves encouraging them to seek help, being understanding of their challenges, and promoting a conducive sleep environment.
In summary, understanding the various treatment options for sleep disorders is essential for effective management. If you suspect you have a sleep disorder, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for guidance and support. Prioritizing sleep health can lead to significant improvements in overall well-being and quality of life.
 Clinic Booking
Clinic Booking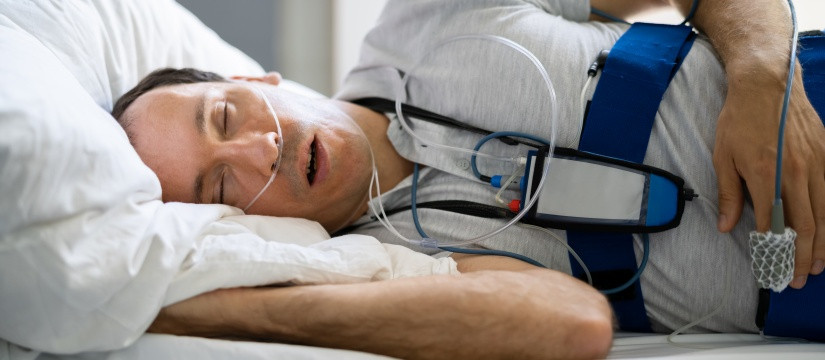


 No Record
No Record