Scars are a natural part of the body's healing process, forming when the skin repairs itself after an injury, surgery, or skin condition like acne. While some scars fade over time, others can be more noticeable and persistent, prompting many to seek treatment. Fortunately, advancements in dermatology and cosmetic surgery have made it possible to treat various types of scars. Understanding the type of scar you have is crucial to determining the best treatment. This complete guide outlines the different types of scars and the available treatments for each.
1. Atrophic Scars
Atrophic scars are sunken scars that sit below the surrounding skin level, often resulting from conditions like acne or chickenpox. These scars occur when there is a loss of tissue during the healing process, leaving behind a pitted appearance.
Treatment Options:
- Dermal Fillers: Injectable fillers can temporarily raise the scar to the same level as the surrounding skin, making it less noticeable.
- Microneedling: This procedure stimulates collagen production, helping to improve the appearance of atrophic scars.
- Chemical Peels: A chemical solution is applied to the skin to exfoliate the surface, which can help reduce the depth and visibility of atrophic scars.
- Laser Resurfacing: Fractional lasers can smooth the skin's surface and promote collagen growth, improving the appearance of sunken scars.
2. Hypertrophic Scars
Hypertrophic scars are raised, red scars that form within the boundaries of the original wound. They are caused by an overproduction of collagen during the healing process. While they may improve over time, hypertrophic scars can remain elevated and discolored for years.
Treatment Options:
- Steroid Injections: Corticosteroid injections can help flatten hypertrophic scars and reduce redness and swelling.
- Silicone Sheets or Gels: Applying silicone sheets or gels can hydrate the scar tissue, making it softer and less noticeable over time.
- Laser Therapy: Pulsed-dye lasers target blood vessels in the scar tissue, reducing redness and promoting a flatter appearance.
- Cryotherapy: In some cases, freezing the scar tissue with liquid nitrogen can reduce its size.
3. Keloid Scars
Keloid scars are similar to hypertrophic scars but grow beyond the boundaries of the original wound. These scars are thick, raised, and often darker in color than the surrounding skin. Keloids can be itchy, painful, and more difficult to treat than other types of scars due to their aggressive growth.
Treatment Options:
- Surgical Removal: Keloid scars can be surgically removed, though there is a risk of the scar returning, often larger than before.
- Radiation Therapy: After surgical removal, radiation therapy may be used to prevent the keloid from regrowing.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing keloids can reduce their size and flatten the scar.
- Steroid Injections: Like hypertrophic scars, keloids can be treated with corticosteroid injections to shrink the scar and alleviate discomfort.
- Laser Therapy: Lasers can reduce the size and redness of keloids, though multiple sessions may be necessary.
4. Contracture Scars
Contracture scars form when the skin is severely burned or damaged, causing the skin to tighten and contract. These scars can limit movement and affect deeper tissues such as muscles and nerves. Contracture scars are often the result of second- or third-degree burns.
Treatment Options:
- Surgery: In severe cases, contracture scars may require surgical procedures like skin grafts or flap surgery to restore mobility and improve the appearance.
- Physical Therapy: Stretching and exercise can help improve mobility and reduce the tightness caused by contracture scars.
- Laser Therapy: Fractional laser treatments can help soften the scar tissue and improve its appearance.
5. Acne Scars
Acne scars can vary in appearance and type, ranging from atrophic scars (such as icepick, boxcar, or rolling scars) to hyperpigmented spots. Acne scars result from inflamed blemishes that damage the skin's underlying tissue.
Treatment Options:
- Microneedling: A popular treatment for acne scars, microneedling stimulates collagen production to improve the skin’s texture.
- Chemical Peels: Depending on the depth of the acne scars, a chemical peel can help reduce their visibility.
- Laser Resurfacing: Fractional or CO2 lasers target the damaged skin to smooth out acne scars and encourage collagen formation.
- Subcision: This minimally invasive procedure breaks up the fibrous bands of tissue that cause the skin to depress, improving the appearance of rolling scars.
6. Surgical Scars
Surgical scars are inevitable after undergoing any type of surgery. While some surgical scars heal well and fade over time, others may become raised, wide, or discolored.
Treatment Options:
- Silicone Sheets or Gels: Applying silicone products can help reduce the size, thickness, and redness of surgical scars.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can target both the texture and pigmentation of surgical scars, making them less visible.
- Scar Revision Surgery: In some cases, a plastic surgeon may recommend scar revision surgery to improve the appearance of surgical scars, especially if they are raised or improperly healed.
7. Stretch Marks
Stretch marks are a type of scar that occurs when the skin is stretched rapidly due to pregnancy, weight gain, or growth spurts. These marks are often red or purple initially but fade to white over time.
Treatment Options:
- Laser Therapy: Fractional lasers or pulsed-dye lasers can reduce the appearance of stretch marks by promoting collagen production and skin regeneration.
- Microneedling: This treatment stimulates collagen and elastin, helping to reduce the visibility of stretch marks.
- Topical Retinoids: Prescription creams containing retinoids can help fade newer stretch marks, though they are less effective on older marks.
8. Hyperpigmented Scars
Some scars leave behind dark spots or patches of skin known as hyperpigmentation. These scars occur when the skin produces excess melanin in response to an injury or inflammation.
Treatment Options:
- Topical Lightening Agents: Products containing ingredients like hydroquinone, vitamin C, or licorice extract can help lighten dark scars.
- Chemical Peels: Mild to moderate peels can exfoliate the skin and reduce hyperpigmentation over time.
- Laser Therapy: Lasers targeting melanin can break up the pigment in hyperpigmented scars, helping to restore an even skin tone.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the most common types of scars?
The most common types of scars include atrophic scars, hypertrophic scars, keloid scars, and contracture scars.
2. Can all scars be treated?
While not all scars can be completely removed, many can be significantly improved with treatments like laser therapy, microneedling, and surgical procedures.
3. How long does it take for a scar to heal?
Scars can take months or even years to fully heal. The healing process depends on the type of scar and the treatment method used.
4. Is laser therapy effective for all types of scars?
Laser therapy is effective for many types of scars, including acne scars, hypertrophic scars, and surgical scars. However, multiple sessions may be required for optimal results.
5. Can stretch marks be fully removed?
Stretch marks are a type of scar and, while they can be faded significantly, they cannot be completely removed.
6. How soon after an injury should I start treating a scar?
It’s best to start treating a scar as soon as the wound has healed and closed. Early treatment can prevent the scar from becoming more prominent.
7. Are home remedies effective for scar treatment?
Home remedies, such as vitamin E oil and aloe vera, may help improve the appearance of scars but are generally less effective than professional treatments.
8. Do scars get worse with age?
Some scars may fade over time, while others can become more noticeable as the skin loses elasticity with age. Treatments like laser therapy can help manage these changes.
9. Can keloid scars be prevented?
While keloid scars are difficult to prevent, certain precautions—such as using silicone sheets after surgery or injury—can help reduce their development.
10. Is scar treatment covered by insurance?
Most insurance companies do not cover scar treatments unless they are medically necessary. Treatments performed for cosmetic reasons are typically not covered.
Whether caused by surgery, injury, or skin conditions, scars are a common part of life. With a range of treatments available, you don’t have to live with scars that affect your appearance or comfort. Consult a dermatologist or plastic surgeon to determine the best treatment option for your specific type of scar.
 Clinic Booking
Clinic Booking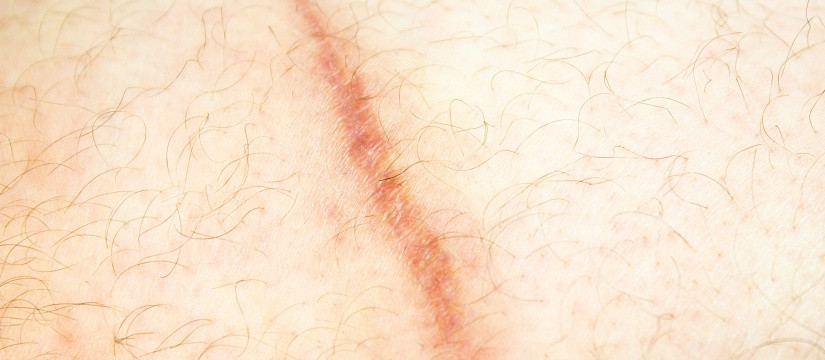


 No Record
No Record