Heart rhythm disorders, also known as arrhythmias, are abnormalities in the heart's electrical system that disrupt the normal rhythm of the heartbeat. These conditions can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications, affecting the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. This article provides an overview of heart rhythm disorders, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
1. Understanding Heart Rhythm Disorders
1.1 What Are Heart Rhythm Disorders?
Definition: Heart rhythm disorders occur when the electrical signals that coordinate heartbeats are disrupted, causing the heart to beat too quickly (tachycardia), too slowly (bradycardia), or irregularly (arrhythmia).
Types: There are several types of arrhythmias, including:
- Atrial Fibrillation: A rapid, irregular heartbeat that can increase the risk of stroke.
- Atrial Flutter: Similar to atrial fibrillation but with a more organized rhythm.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: A fast heartbeat originating from the lower chambers of the heart.
- Ventricular Fibrillation: A life-threatening condition where the heart quivers instead of pumping effectively.
- Bradycardia: A slow heart rate, often defined as fewer than 60 beats per minute.
2. Causes of Heart Rhythm Disorders
2.1 Underlying Heart Conditions
- Coronary Artery Disease: Reduced blood flow to the heart can lead to arrhythmias.
- Heart Valve Disorders: Malfunctioning heart valves can disrupt normal blood flow, affecting heart rhythm.
- Heart Failure: Weakened heart muscles can lead to abnormal electrical signaling.
2.2 Other Factors
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Abnormal levels of potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium can disrupt the heart's electrical system.
- Medications: Certain medications can cause or exacerbate arrhythmias.
- Alcohol and Drug Use: Excessive alcohol consumption and recreational drug use (e.g., cocaine) can trigger arrhythmias.
- Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can affect heart rhythm.
3. Symptoms of Heart Rhythm Disorders
3.1 Common Symptoms
Patients with heart rhythm disorders may experience a variety of symptoms, including:
- Palpitations: A sensation of a racing, fluttering, or pounding heartbeat.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: A feeling of faintness or unsteadiness, especially during physical activity.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling winded, even with minimal exertion.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest, which can range from mild to severe.
- Fatigue: Unusual tiredness or lack of energy, often related to the heart's reduced efficiency.
3.2 Severe Symptoms
In some cases, arrhythmias can lead to more severe symptoms, including:
- Loss of Consciousness: Fainting or passing out due to inadequate blood flow to the brain.
- Heart Attack Symptoms: Chest pain, radiating pain to the arms or jaw, and excessive sweating may indicate a heart attack.
4. Diagnosis of Heart Rhythm Disorders
4.1 Medical History and Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will typically begin with a thorough medical history and physical examination, focusing on the patient’s symptoms and any underlying health conditions.
4.2 Diagnostic Tests
Common tests used to diagnose heart rhythm disorders include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): A test that records the electrical activity of the heart and helps identify arrhythmias.
- Holter Monitor: A portable ECG device worn for 24 to 48 hours to capture heart rhythms over time.
- Event Monitor: Similar to a Holter monitor, but worn for longer periods and activated by the patient when symptoms occur.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart that assesses its structure and function, helping identify underlying heart conditions.
5. Treatment Options for Heart Rhythm Disorders
5.1 Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Diet: Eating a heart-healthy diet can help manage underlying conditions that contribute to arrhythmias.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart rhythm disorders.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and anxiety levels.
5.2 Medications
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: These medications help restore normal heart rhythm and prevent episodes of arrhythmia.
- Beta-Blockers: Used to slow down the heart rate and reduce blood pressure, which can help manage certain arrhythmias.
- Anticoagulants: Blood-thinning medications may be prescribed for patients with atrial fibrillation to reduce the risk of stroke.
5.3 Medical Procedures
- Cardioversion: A procedure that uses electrical shock to restore normal heart rhythm, often performed in a hospital setting.
- Catheter Ablation: A minimally invasive procedure that destroys abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that cause arrhythmias.
- Pacemaker: A small device implanted under the skin that helps regulate the heartbeat in patients with bradycardia or other rhythm disorders.
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD): A device implanted in patients at risk of life-threatening arrhythmias, designed to monitor heart rhythm and deliver shocks if necessary.
5.4 Surgery
In some cases, more invasive surgical options may be required to treat arrhythmias, especially when other treatments are ineffective.
Heart rhythm disorders can significantly impact the heart's ability to function effectively, leading to a variety of symptoms and complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike. With proper diagnosis and management, individuals with heart rhythm disorders can lead healthy and active lives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the most common types of heart rhythm disorders?
Common types include atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and bradycardia.
2. What causes heart rhythm disorders?
Causes can include underlying heart conditions, electrolyte imbalances, certain medications, lifestyle factors, and stress.
3. How are heart rhythm disorders diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a medical history review, physical examination, and tests such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) and Holter monitors.
4. What symptoms should I look for?
Common symptoms include palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue. Severe symptoms may include fainting or signs of a heart attack.
5. What lifestyle changes can help manage heart rhythm disorders?
Adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress, and avoiding stimulants can help manage arrhythmias.
6. What types of medications are used to treat heart rhythm disorders?
Antiarrhythmic drugs, beta-blockers, and anticoagulants are commonly used to manage these conditions.
7. Are there medical procedures available for treating arrhythmias?
Yes, procedures such as cardioversion, catheter ablation, pacemaker implantation, and ICD placement may be recommended depending on the severity of the condition.
8. Can heart rhythm disorders be cured?
While some arrhythmias can be effectively managed or treated, others may be chronic and require ongoing management.
9. How can I reduce my risk of developing heart rhythm disorders?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing existing health conditions, and avoiding excessive alcohol and stimulants can help reduce the risk.
10. When should I seek medical attention for heart rhythm concerns?
If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, such as palpitations, chest pain, or shortness of breath, seek medical attention promptly.
 Clinic Booking
Clinic Booking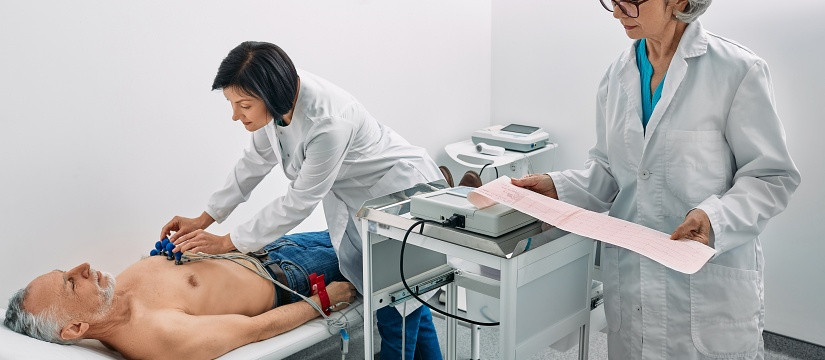


 No Record
No Record