In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a groundbreaking assisted reproductive technology (ART) that has transformed the lives of countless individuals and couples facing infertility challenges. This method involves a series of sophisticated medical procedures aimed at facilitating pregnancy by manually combining an egg and sperm in a laboratory setting. This comprehensive article explores the intricacies of the IVF process, its numerous benefits, potential risks, and a comprehensive FAQ section to address common queries related to this innovative fertility treatment.
1. Understanding IVF
In vitro fertilization, which translates to "fertilization in glass," refers to the laboratory environment where the fertilization process takes place. IVF is a multifaceted approach to infertility treatment, encompassing several steps, from ovarian stimulation to embryo transfer. Below is a detailed breakdown of the IVF process:
1.1. Ovarian Stimulation
The IVF journey begins with ovarian stimulation, wherein hormonal medications are administered to encourage the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. This is a critical step, as having several eggs increases the chances of successful fertilization. The medication regimen typically includes gonadotropins, which are injected subcutaneously. Throughout this phase, patients undergo regular monitoring, including blood tests and ultrasounds, to track hormone levels and the development of ovarian follicles.
1.2. Egg Retrieval
Once the eggs have reached maturity, a minor surgical procedure known as transvaginal ultrasound aspiration is performed to retrieve them. This procedure is usually conducted under sedation or anesthesia to minimize discomfort. A thin needle is inserted through the vaginal wall into the ovaries, allowing the physician to extract the mature eggs carefully.
1.3. Sperm Collection
While the eggs are being retrieved, sperm is collected from the male partner or a sperm donor. This sample is then processed in the laboratory to isolate the healthiest and most viable sperm for fertilization. If there are issues with sperm quality or quantity, advanced techniques like sperm washing or even surgical retrieval may be employed.
1.4. Fertilization
Following egg retrieval, the mature eggs are placed in a culture dish with the prepared sperm. Fertilization can occur through traditional insemination, where sperm is allowed to swim to the egg, or through intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), a more advanced technique where a single sperm is injected directly into an egg. The fertilized eggs, now called embryos, are monitored for development over the next few days, typically for three to five days.
1.5. Embryo Transfer
Once the embryos have developed, one or more are selected for transfer into the uterus. This process is called embryo transfer and is performed using a thin catheter. It is a relatively simple procedure that typically requires no anesthesia, although some patients may experience mild discomfort. The number of embryos transferred can vary based on individual circumstances, including the patient's age and previous IVF attempts.
1.6. Pregnancy Test
Approximately two weeks after the embryo transfer, a blood test is conducted to determine if pregnancy has occurred. If the test result is positive, the patient will continue with prenatal care to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
2. Benefits of IVF
IVF offers numerous advantages for individuals and couples facing infertility challenges:
2.1. High Success Rates
IVF has higher success rates compared to many other fertility treatments. Factors such as age, the cause of infertility, and the quality of embryos all play a role in determining success. For many, IVF presents the best chance of achieving pregnancy, especially when traditional methods have failed.
2.2. Genetic Screening
One of the significant benefits of IVF is the option for preimplantation genetic testing (PGT). This allows potential parents to screen embryos for genetic disorders before transfer, significantly reducing the risk of inherited conditions and ensuring healthier pregnancies.
2.3. Donor Options
IVF facilitates the use of donor eggs or sperm, providing opportunities for those with severe infertility issues, such as diminished ovarian reserve or male factor infertility, to achieve pregnancy.
2.4. Flexibility and Control
IVF offers flexibility, allowing couples to make informed decisions about their treatment options. This includes the ability to select the number of embryos to transfer and the option to freeze any surplus embryos for future use, giving individuals control over their family planning.
2.5. Same-Sex Couples and Single Parents
IVF is an essential option for same-sex couples and single individuals wishing to conceive. It allows them to explore parenthood through donor sperm or eggs, ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to build a family.
3. Risks and Considerations
While IVF is generally safe and effective, it is essential to be aware of potential risks and considerations:
3.1. Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
Some women may experience ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) due to an excessive response to fertility medications. This condition can lead to symptoms such as swollen and painful ovaries, fluid accumulation in the abdomen, and, in severe cases, serious complications.
3.2. Multiple Pregnancies
IVF increases the likelihood of multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, etc.), which can lead to higher risks for both the mother and babies. Multiple gestations often result in increased healthcare needs, potential complications during pregnancy, and premature birth.
3.3. Emotional and Financial Stress
The IVF process can be emotionally and financially taxing. Individuals and couples may face challenges related to the emotional ups and downs of treatment and the costs associated with multiple cycles. It's essential for patients to seek support and counseling to navigate these challenges effectively.
3.4. Ectopic Pregnancy
There is a risk of ectopic pregnancy, where the embryo implants outside the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube. This condition requires immediate medical attention, as it can pose serious health risks to the individual.
3.5. Long-Term Health Risks
While extensive research has been conducted on IVF, some studies have suggested a potential association between IVF and certain health risks, including low birth weight and developmental issues. However, more research is needed to draw definitive conclusions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How long does the IVF process take?
The IVF process can take several weeks from ovarian stimulation to embryo transfer, with additional time required for pregnancy testing. Typically, a complete IVF cycle lasts about 4 to 6 weeks.
2. How much does IVF cost?
The cost of IVF varies significantly based on location, clinic, and specific treatments required. On average, the total cost can range from $10,000 to $15,000 per cycle, excluding medications and any additional procedures.
3. Is IVF painful?
Egg retrieval may cause discomfort, but most patients experience minimal pain during the procedure due to sedation. Post-procedure discomfort may include cramping, which usually subsides within a few days.
4. What are the chances of success with IVF?
Success rates depend on various factors, including age, underlying fertility issues, and the number of embryos transferred. On average, success rates range from 20% to 50% per cycle, with higher rates for younger women.
5. Can IVF be done with a single embryo?
Yes, many clinics practice single embryo transfer (SET) to reduce the risk of multiple pregnancies while maintaining high success rates. SET is especially recommended for younger patients with good-quality embryos.
6. Are there age limits for IVF?
While there are no strict age limits, success rates decline significantly after the age of 35. Many clinics have upper age limits for egg retrieval, often around 42 to 45 years, depending on individual circumstances.
7. What happens to unused embryos?
Unused embryos may be frozen for future use, donated to other couples, or disposed of based on the patients' wishes. Many couples choose to freeze their embryos for potential future pregnancies.
8. How long should I wait before doing IVF again if the first cycle is unsuccessful?
Patients are usually advised to wait one to three menstrual cycles before attempting another IVF cycle. This waiting period allows the body to recover physically and emotionally.
9. Can I travel during the IVF process?
Travel is generally permitted during the IVF process, but it’s advisable to stay close to the fertility clinic during key procedures, especially around the time of egg retrieval and embryo transfer.
10. What lifestyle changes should I consider before starting IVF?
Healthy lifestyle changes can positively impact IVF success. Patients are encouraged to maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and manage stress through mindfulness or counseling.
11. How many IVF cycles are typically needed for success?
The number of IVF cycles required for success varies widely among individuals. While some may achieve pregnancy in one cycle, others may need multiple attempts, with many clinics recommending up to three cycles before considering further evaluation or alternative options.
12. Can I use my own eggs if I am older?
Women over the age of 35 can still use their own eggs for IVF; however, the success rates may be lower. Clinics often discuss the option of using donor eggs if the patient's egg quality is a concern.
13. What is the difference between IVF and IUI?
IVF and intrauterine insemination (IUI) are both fertility treatments, but they differ in their approaches. IVF involves the fertilization of eggs outside the body, while IUI involves placing sperm directly into the uterus during ovulation without laboratory fertilization.
14. How do I choose a fertility clinic for IVF?
Choosing a fertility clinic for IVF involves researching success rates, patient reviews, available treatments, and the expertise of the medical staff. It's crucial to schedule consultations to find a clinic that aligns with your needs and comfort level.
15. What should I expect during the embryo transfer process?
During embryo transfer, the physician will use a thin catheter to place the selected embryo(s) into the uterus. The procedure is quick, typically taking about 10 to 15 minutes, and most patients can resume normal activities shortly afterward.
In conclusion, IVF is a revolutionary solution for individuals and couples experiencing infertility, offering hope and the possibility of parenthood. Understanding the IVF process, its benefits, and potential risks is crucial for making informed decisions. If you are considering IVF, consulting with a qualified fertility specialist is essential to discuss your options and develop a personalized treatment plan. The journey may be challenging, but many couples find that the joy of a successful pregnancy makes it all worthwhile. With advancements in technology and medical practices, IVF continues to evolve, providing even greater possibilities for those on the path to parenthood.
 Clinic Booking
Clinic Booking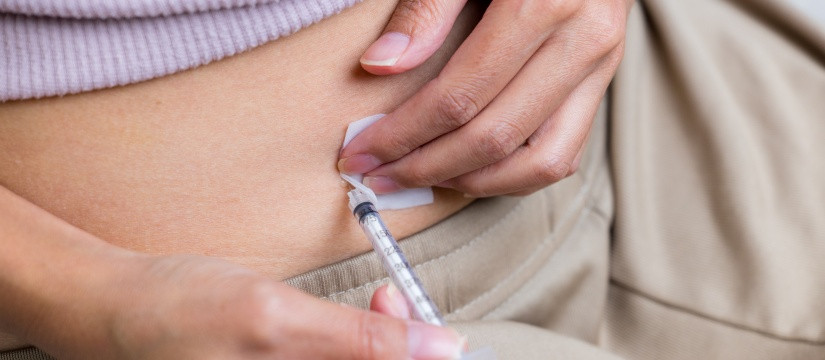


 No Record
No Record