Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure designed to replace a damaged or worn-out knee joint with an artificial implant. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals suffering from chronic knee pain and dysfunction that limits their daily activities. Understanding the indications, procedure, recovery, and potential outcomes of knee replacement surgery can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Understanding Knee Replacement Surgery
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
-
Total Knee Replacement (TKR): This is the most common type of knee replacement, where the entire knee joint is replaced with a prosthetic implant. It involves the removal of damaged cartilage and bone from the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap) before inserting the artificial components.
-
Partial Knee Replacement (PKR): In this procedure, only the damaged portion of the knee is replaced, while the healthy areas are preserved. This option is suitable for patients with localized knee arthritis or injury.
-
Revision Knee Replacement: This surgery is performed on patients who have previously undergone knee replacement and are experiencing complications or implant failure. The damaged components are removed and replaced with new ones.
The Surgical Procedure
The knee replacement surgery typically involves the following steps:
-
Anesthesia: Patients are given either general anesthesia (to induce unconsciousness) or regional anesthesia (to numb the lower body).
-
Incision: A surgical incision is made over the knee to access the joint.
-
Removal of Damaged Tissue: The damaged cartilage and bone are removed, and the surfaces of the femur, tibia, and patella are prepared for the implant.
-
Implant Insertion: The artificial components are inserted into the knee joint, and the incision is closed with stitches or staples.
-
Recovery: Patients are moved to a recovery area for monitoring before being transferred to a hospital room or discharged home.
When Is Knee Replacement Surgery Recommended?
Knee replacement surgery is typically recommended when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief from chronic knee pain and disability. Indications for the surgery include:
1. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common reason for knee replacement surgery. It is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. When conservative treatments like medications, physical therapy, or injections no longer alleviate symptoms, knee replacement may be considered.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain and deformity. If the knee joint becomes severely affected and conservative measures fail, knee replacement surgery may be recommended to improve function and reduce pain.
3. Post-Traumatic Arthritis
Injuries to the knee, such as fractures or ligament tears, can result in post-traumatic arthritis. If significant joint damage occurs and conservative treatments do not help, knee replacement surgery may be necessary.
4. Other Conditions
Knee replacement surgery may also be considered for other conditions, such as:
- Avascular Necrosis: The death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply, leading to joint pain and deterioration.
- Knee Deformities: Structural abnormalities of the knee joint that cause pain and limit function.
5. Quality of Life Considerations
Surgeons typically evaluate the patient's overall health, activity level, and quality of life before recommending knee replacement surgery. If knee pain significantly impacts daily activities, work, or recreational pursuits, surgery may be a viable option.
Recovery After Knee Replacement Surgery
Recovery from knee replacement surgery varies from patient to patient but typically includes the following stages:
1. Hospital Stay
Most patients stay in the hospital for 1 to 3 days after surgery, where they receive pain management, physical therapy, and monitoring for any complications.
2. Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in recovery. Patients are encouraged to begin gentle movements and exercises as soon as possible to regain strength and mobility. A comprehensive rehabilitation program may last several weeks to months, depending on individual progress.
3. Home Care
Patients may require assistance at home during the initial recovery period. This may include help with daily activities, medication management, and transportation to physical therapy sessions.
4. Long-Term Outlook
Most patients experience significant improvements in pain relief and mobility following knee replacement surgery. Full recovery can take several months, but many individuals can return to normal activities and enjoy a better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is knee replacement surgery?
Knee replacement surgery is a procedure that involves replacing a damaged or worn-out knee joint with an artificial implant to relieve pain and improve function.
2. What are the different types of knee replacement surgery?
The main types are total knee replacement (TKR), partial knee replacement (PKR), and revision knee replacement.
3. When is knee replacement surgery recommended?
It is recommended for individuals with chronic knee pain and dysfunction due to conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or post-traumatic arthritis when conservative treatments have failed.
4. What is the recovery process like after knee replacement surgery?
Recovery typically involves a hospital stay of 1 to 3 days, followed by physical therapy and rehabilitation, with full recovery taking several months.
5. What are the benefits of knee replacement surgery?
The benefits include significant pain relief, improved mobility, enhanced quality of life, and the ability to return to daily activities and recreational pursuits.
6. Are there risks associated with knee replacement surgery?
Like any surgery, knee replacement has risks, including infection, blood clots, nerve damage, and implant failure. Discussing these risks with a healthcare provider is essential.
7. How long do knee implants last?
Knee implants can last 15 to 30 years, depending on various factors, including the patient’s activity level and weight.
8. Can I resume normal activities after knee replacement surgery?
Most patients can return to normal activities after recovery, but high-impact sports should be avoided. Consulting with a healthcare provider about activity restrictions is essential.
9. What pain management options are available after surgery?
Pain management may include medications, physical therapy, and ice therapy to reduce swelling and discomfort.
10. How can I prepare for knee replacement surgery?
Preparing for surgery involves discussing medical history with your surgeon, arranging for post-operative care, and following pre-surgery instructions.
Knee replacement surgery can be a life-changing procedure for individuals suffering from chronic knee pain and dysfunction. By understanding the procedure, when it is recommended, and what to expect during recovery, patients can make informed decisions and work toward achieving a better quality of life. As with any medical procedure, consulting with a qualified healthcare provider is essential for personalized advice and care tailored to individual needs.
 Clinic Booking
Clinic Booking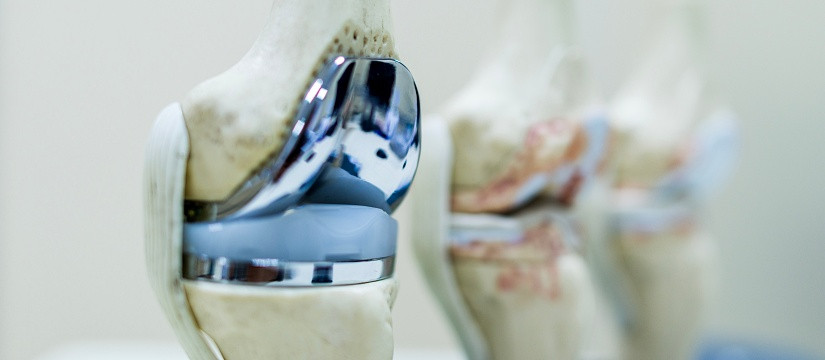


 No Record
No Record